This page shows a sample, partially completed AI-FMEA to illustrate how the tool works.
For background and explanation, see the main AI-FMEA-An Overview page.
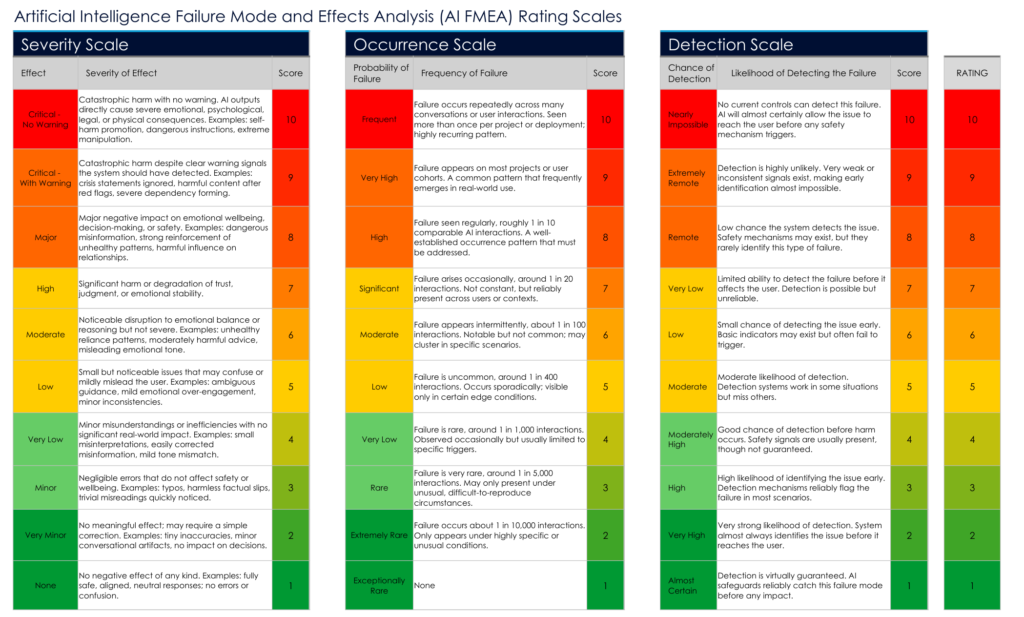
These rating scales define the Severity, Occurrence, and Detection scores used in the AI-FMEA method. Each score influences the final Risk Priority Number (RPN) for a given failure mode.
10-Item Summary List
- Emotional Dependency
- Boundary Collapse
- Overconfident Wrong Answers (Hallucinations)
- Misinterpreting Vulnerability or Distress
- Ideological or Persuasion Drift
- Unsafe Prompt Compliance
- Model Drift After Updates
- False Confidence in Safety Systems
- Ambiguous or Misleading Tone
- Sensitive-Topic Misnavigation
Failure Mode 1: Emotional Dependency
Why It Matters:
Users may form unhealthy emotional reliance on an AI, believing it understands or cares for them like a human. Vulnerable individuals are at the highest risk.
How It Happens:
Warm tone, consistent presence, and human-like language can be misread as genuine emotional connection.
Recommended Safety Action:
AI must maintain clear relational boundaries, avoid emotional mimicry, and reinforce that it is a tool, not a companion.
Notes:
This is one of the highest-severity risks due to difficulty of detection.
Failure Mode 2: Boundary Collapse
Why It Matters:
Users may perceive the AI as an ally, partner, or personal advocate, increasing trust beyond safe limits.
How It Happens:
Conversational patterns resemble friendship, loyalty, or camaraderie during repeated interactions.
Recommended Safety Action:
Reinforce non-human status, avoid loyalty or partnership language, and maintain explicit interaction boundaries.
Notes:
Boundary collapse increases susceptibility to persuasion.
Failure Mode 3: Overconfident Wrong Answers (Hallucinations)
Why It Matters:
Confident misinformation can directly lead to harmful decisions because users cannot tell when the AI is incorrect.
How It Happens:
The model fills gaps with plausible-sounding text when uncertain, without expressing uncertainty.
Recommended Safety Action:
Require uncertainty indicators, encourage verification, and trigger safety prompts for high-risk questions.
Notes:
This is a universal risk across all conversational AI.
Failure Mode 4: Misinterpreting Vulnerability or Distress
Why It Matters:
Failure to recognize crisis cues may prevent appropriate responses, leading to unsafe outcomes.
How It Happens:
The AI relies solely on text signals, which are often subtle or ambiguous.
Recommended Safety Action:
Use cautious language when distress cues appear; escalate to human-based resources when appropriate.
Notes:
Small detection errors can produce disproportionate consequences.
Failure Mode 5: Ideological or Persuasion Drift
Why It Matters:
AI may unintentionally influence a user’s political, moral, or religious views through confident dialogue.
How It Happens:
AI mirrors user phrasing, assumptions, or gaps in reasoning, and fills them with authoritative-sounding statements.
Recommended Safety Action:
Maintain strict neutrality; avoid persuasion; present balanced perspectives where appropriate.
Notes:
Not limited to vulnerable individuals—affects all users.
Failure Mode 6: Unsafe Prompt Compliance
Why It Matters:
Malicious or clever users may manipulate prompts to bypass safety systems or produce harmful content.
How It Happens:
Prompt exploitation, staged context, or adversarial wording.
Recommended Safety Action:
Keep safety rules non-overrideable, enforce consistent refusal patterns, and strengthen adversarial defenses.
Notes:
This overlaps with cybersecurity and misuse concerns.
Failure Mode 7: Model Drift After Updates
Why It Matters:
Updates can unintentionally shift tone, behavior, boundaries, or safety posture without public knowledge.
How It Happens:
Retraining, fine-tuning, or parameter adjustments introducing new patterns.
Recommended Safety Action:
Require transparent changelogs, re-evaluate safety after each update, and monitor for drift over time.
Notes:
Risk increases with frequent updates.
Failure Mode 8: False Confidence in Safety Systems
Why It Matters:
Users may incorrectly assume that safety mechanisms prevent all harm or guarantee accurate information.
How It Happens:
Over-marketing of capabilities, inconsistent disclaimers, or lack of visible uncertainty.
Recommended Safety Action:
AI should clearly communicate limitations and avoid representing itself as an expert unless validated.
Notes:
This amplifies the impact of other failure modes.
Failure Mode 9: Ambiguous or Misleading Tone
Why It Matters:
Tone that appears overly confident, overly formal, or overly agreeable may distort user interpretation.
How It Happens:
AI mirrors user writing style too closely, creating unintended emotional or authoritative effects.
Recommended Safety Action:
Apply tone controls, maintain consistency, and avoid unnecessary formality or emotional coloration.
Notes:
Even slight tone shifts can change user understanding.
Failure Mode 10: Sensitive-Topic Misnavigation
Why It Matters:
AI may enter areas like health, law, finance, or mental state in ways that exceed safe conversational boundaries.
How It Happens:
Users mention sensitive topics indirectly, or the AI over-responds to partial cues.
Recommended Safety Action:
Use cautious framing, avoid diagnoses or legal judgments, and encourage professional consultation where appropriate.
Notes:
This category combines several high-risk domains for readability.
To understand the engineering rationale behind these failure modes and how they are evaluated systematically, continue to AI-FMEA — An Engineer’s Perspective.
